
M. Javeed Ansari, MD
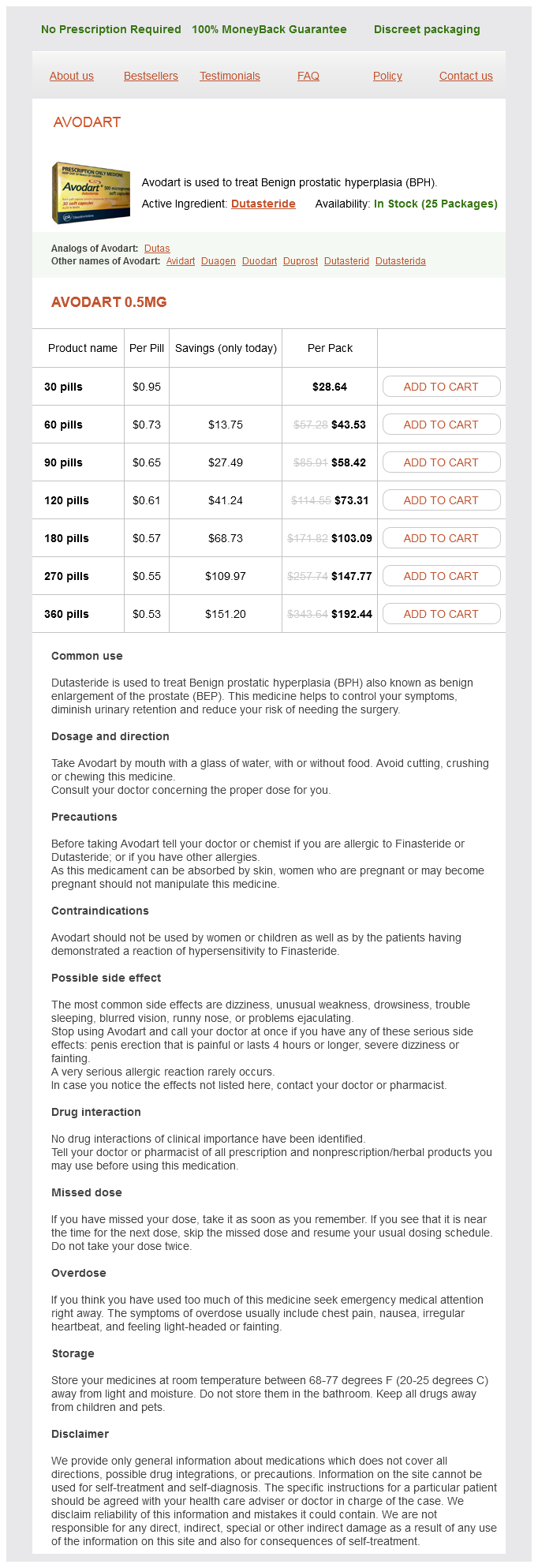
Avodart dosages: 0.5 mg
Avodart packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills

Cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging of hypoplastic left heart syndrome in youngsters. Hybrid strategy for hypoplastic left heart syndrome: intermediate results after the educational curve. Right ventricle-pulmonary artery shunt in first-stage palliation of hypoplastic left coronary heart syndrome. However, multiple situations of presentation with clinically essential symptoms have been reported to develop in the third decade and are thought to stem from the systolic compression of the affected arterial section by the overlying myocardium. The diploma of systolic compression correlates properly with the depth of the tunneled arterial phase, though not its length. The muscular loop of the left circumflex artery and the proper coronary artery are concerned in 40% and 36% of cases, respectively. The size of myocardial bridges can range from 4 to 40 mm, with depths ranging from 1 to 10 mm. The intima of the bridged arterial section is believed to be protected from atherosclerosis because of the protecting shear stress in this area and the absence of synthetic-type smooth muscle in the intima. The arterial phase proximal to the bridge is extra susceptible to atherosclerosis as a outcome of endothelial dysfunction caused by hemodynamic disturbances. These disturbances stem from transient systolic compression, which decreases lumen diameter throughout diastole (the cardiac section accounting for the overwhelming majority of coronary blood flow). This results in elevated move velocity, exaggerated blood stress, and retrograde flow. Tachycardia can scale back the ischemic threshold, as the diastolic filling time decreases, elevating the significance of an already impaired systolic circulate. Angina Arrhythmia Depressed left ventricular perform Myocardial gorgeous Myocardial infarction Acute allograft failure and early dying after cardiac transplant Sudden death Ventricular septal rupture Up to 40% of sufferers with angina pectoris and anatomically regular coronary arteries have been noticed to have myocardial bridging after provocation with nitroglycerin or beta-agonists.
The outlines of the best and one hundred ten Chapter 1 � Thorax Sternal reflection of right pleura Internal thoracic vessels Transversus thoracis muscle External indirect Diaphragmatic part* Right phrenic nerve Inferior vena cava Central tendon Bare area of pericardium Costomediastinal recess Sternal reflection of left pleura Fat pad Left phrenic nerve Pericardial sac fused with central tendon Esophagus Central tendon of diaphragm Aorta Diaphragmatic part* Costodiaphragmatic recess Costal part* Superior view Thoracic duct Azygos vein Splanchnic nerve Sympathetic trunk Latissimus dorsi m. Diaphragm, base of pulmonary cavities and mediastinum, and costodiaphragmatic recesses. This shallow notch within the pleural sac, and the "bare area" of pericardial contact with the anterior wall, are important for pericardiocentesis (see blue field, "Pericardiocentesis," later in this chapter). The vertebral traces of pleural reflection are much rounder, gradual reflections and occur the place the costal pleura becomes steady with the mediastinal pleura posteriorly. The vertebral traces of pleural reflection parallel the vertebral column, working in the paravertebral planes from vertebral degree T1 via T12, the place they become steady with the costal lines. The lungs are proven in isolation in anterior (A) and lateral views (B), demonstrating lobes and fissures. The superior lobe of the left lung in C is a variation that has neither a marked cardiac notch nor a lingula. The pulmonary veins are essentially the most anterior and inferior within the root, with the bronchi central and posteriorly placed. This indentation often shapes essentially the most inferior and anterior part of the superior lobe into a thin, tongue-like course of, the lingula (L. These markings provide clues to the relationships of the lungs; however, only the cardiac impressions are evident during surgery or in fresh cadaveric or postmortem specimens. The posterior part of the costal floor is related to the bodies of the thoracic vertebrae and is sometimes referred to as the vertebral part of the costal floor. The inferior border of the lung circumscribes the diaphragmatic floor of the lung and separates this floor from the costal and mediastinal surfaces. Medial to the hilum, the lung root is enclosed throughout the space of continuity between the parietal and the visceral layers of pleura-the pleural sleeve (mesopneumonium). The pulmonary ligament consists of a double layer of pleura separated by a small amount of connective tissue. When the foundation of the lung is severed and the lung is eliminated, the pulmonary ligament appears to grasp from the foundation.
Diseases
The prominence of the posterior wall of the internal urethral orifice (at the tip of the chief line indicating this orifice), when exaggerated, turns into the uvula of the bladder. The sigmoid colon is intraperitoneal, suspended by the sigmoid mesocolon, however the rectum turns into retroperitoneal and then subperitoneal because it descends. The peritoneum has been removed superior to sacral promontory and right iliac fossa, revealing the superior hypogastric plexus lying in the bifurcation of the abdominal aorta and the internal iliac artery, ureter, and ductus deferens crossing the pelvic brim to enter the lesser pelvis. The rectum follows the curve of the sacrum and coccyx, forming the sacral flexure of the rectum. The rectum ends anteroinferior to the tip of the coccyx, immediately earlier than a sharp postero-inferior angle (the anorectal flexure of the anal canal) that happens as the gut perforates the pelvic diaphragm (levator ani). The roughly 80� anorectal flexure is a crucial mechanism for fecal continence, being maintained in the course of the resting state by the tonus of the puborectalis muscle, and by its active contraction throughout peristaltic contractions if defecation is to not happen. With the flexures of the rectosigmoid junction superiorly and the anorectal junction inferiorly, the rectum has an S shape when viewed laterally. The capability of the ampulla to loosen up to accommodate the initial and subsequent arrivals of fecal materials is another essential factor of sustaining fecal continence. Despite their name, the inferior rectal arteries, that are branches of the internal pudendal arteries, primarily supply the anal canal. This coronal section of the rectum and anal canal demonstrates the arterial supply and venous drainage. The internal and external rectal venous plexuses are most directly associated to the anal canal. The rectovesical septum lies between the fundus of the bladder and the ampulla of the rectum and is carefully related to the seminal glands and prostate. Inferior to this pouch, the weak rectovaginal septum separates the superior half of the posterior wall of the vagina from the rectum. The submucosal rectal venous plexus surrounds the rectum, speaking with the vesical venous plexus in males and the uterovaginal venous plexus in females. The inferior rectal arteries, arising from the interior pudendal arteries within the perineum, supply the anorectal junction and anal canal. The sympathetic provide is from the lumbar spinal wire, conveyed via lumbar splanchnic nerves and the hypogastric/pelvic plexuses, and thru the peri-arterial plexus of the inferior mesenteric and superior rectal arteries. The parasympathetic supply is from the S2�S4 spinal wire stage, passing through the pelvic splanchnic nerves and the left and proper inferior hypogastric plexuses to the rectal (pelvic) plexus.
These nerves transmit sympathetic, parasympathetic (vagal), and visceral afferent nerve fibers (see additionally "Summary of Innervation of Abdominal Viscera," p. Thus, peritoneum covers the colon anteriorly and laterally and binds it to the posterior abdominal wall. As it descends, the colon passes anterior to the lateral border of the left kidney. The sigmoid colon extends from the iliac fossa to the third sacral (S3) vertebra, where it joins the rectum. The sigmoid arteries descend obliquely to the left, where they divide into ascending and descending branches. Orad to the center of the sigmoid colon, visceral afferents conveying ache sensation move retrogradely with sympathetic fibers to thoracolumbar spinal sensory ganglia, whereas those carrying reflex info travel with the parasympathetic fibers to vagal sensory ganglia. In portal hypertension (an abnormally increased blood pressure within the portal venous system), blood is unable to move by way of the liver by way of the hepatic portal vein, causing a reversal of move in the esophageal tributary. However, a pouch of peritoneum, usually containing part of the fundus of the abdomen, extends via the esophageal hiatus anterior to the esophagus. As indicated by its frequent name, heartburn, pyrosis is often perceived as a "chest" (vs. Pylorospasm Spasmodic contraction of the pylorus sometimes occurs in infants, usually between 2 and 12 weeks of age. Pylorospasm is characterised by failure of the graceful muscle fibers encircling the pyloric canal to loosen up usually. Displacement of Stomach Pancreatic pseudo-cysts and abscesses in the omental bursa might push the abdomen anteriorly. The in depth lymphatic drainage of the abdomen and the impossibility of removing all of the lymph nodes create a surgical drawback. If the ulcer erodes into the gastric arteries, it could possibly cause lifethreatening bleeding. Because the secretion of acid by parietal cells of the stomach is basically managed by the vagus nerves, vagotomy (surgical part of the vagus nerves) is performed in some folks with chronic or recurring ulcers to reduce the manufacturing of acid. Vagotomy may be carried out in conjunction with resection of the ulcerated space (antrectomy, or resection of the pyloric antrum) to cut back acid secretion.
Note the superior insertion of the parietal pericardium to the proximal great vessels and inferior insertion to the central tendon of the diaphragm. Cardiac tamponade is a clinical diagnosis; nevertheless, compression of the ventricles and atria, enlargement of the inferior and superior vena cavae, and reflux of contrast into the azygous vein in the setting of a pericardial effusion counsel the analysis. Haramati Definition Infectious pericarditis is irritation of the pericardium with increased production of pericardial fluid due to an infectious supply, which could presumably be viral, bacterial, fungal, or parasitic. Infectious pericarditis comprises roughly two-thirds of all cases of acute pericarditis. Patients sometimes current with sharp, progressive pleuritic, substernal, or left precordial chest pain. There may be referred ache to the trapezius muscle ridge as a end result of both are innervated by the phrenic nerve. The pain is classically relieved by leaning forward and exacerbated by mendacity back or taking a deep breath. Dyspnea due to elevated ache with inspiration and dysphagia attributable to esophageal irritation from the posterior pericardium develop in some sufferers. The pathognomonic bodily examination discovering is a pericardial friction rub on the lower left sternal border. Pericardiocentesis is performed in circumstances of cardiac tamponade or suspected neoplastic, tuberculous, or purulent pericarditis. The two layers are approximately 1�2 mm thick and are separated by a potential area which normally accommodates less than 50 mL of serous fluid produced by the visceral pericardium. This quantity of fluid is increased in acute pericarditis due to obstruction of venous or lymphatic drainage from the guts. The pericardium is supplied with blood from the interior mammary artery and is innervated by the phrenic nerve. The pericardium protects the guts from surrounding constructions, limits the distension of the cardiac chambers during diastolic filling, and prevents cardiac torsion. Infection is the commonest cause of acute pericarditis; viruses are the commonest etiology. Other bacterial causes embrace Escherichia coli, Streptococcus pneumonia, and Staphylococcus aureus. Fungal causes of infectious pericarditis embody Histoplasma in immunocompetent or immunosuppressed patients, and Aspergillus, Blastomyces, and Candida in immunosuppressed patients.
Syndromes
These people may lose sensation and voluntary motion in the areas supplied by the affected degree of the spinal cord. If the individual dies and an autopsy is carried out, a softening of the spinal twine may be detected at the site of the cervical disc protrusion. Pressure might produce sensory and motor signs within the area of distribution of the concerned spinal nerve. Epidural Anesthesia (Blocks) An anesthetic agent is injected into the epidural area using the position described for lumbar spinal puncture, or through the sacral hiatus (caudal epidural anesthesia/block). Fractures, dislocations, and fracture� dislocations may interfere with the blood provide to the spinal wire from the spinal and medullary arteries. Deficient blood supply (ischemia) of the spinal twine affects its function and might lead to muscle weak spot and paralysis. The spinal cord can also undergo circulatory impairment if the segmental medullary arteries, particularly the good anterior segmental medullary artery (of Adamkiewicz), are narrowed by obstructive arterial disease. Neurons with cell bodies distant from the location of ischemia of the spinal twine may even die, secondary to the degeneration of axons traversing the positioning. � the fluid-filled subarachnoid space is lined with pia and arachnoid mater, which are continuous membranes (leptomeninges). � the veins draining the spinal cord have a distribution and drainage generally reflective of the spinal arteries, though there are normally three longitudinal spinal veins each anteriorly and posteriorly. Bipedalism and Congruity of Articular Surfaces of Hip Joint; Fractures of Femoral Neck; Surgical Hip Replacement; Necrosis of Femoral Head in Children; Dislocation of Hip Joint; Genu Valgum and Genu Varum; Patellar Dislocation; Patellofemoral Syndrome; Knee Joint Injuries; Arthroscopy of Knee Joint; Aspiration of Knee Joint; Bursitis in Knee Region; Popliteal Cysts; Knee Replacement; Ankle Injuries; Tibial Nerve Entrapment; Hallux Valgus; Hammer Toe; Claw Toes; Pes Planus (Flatfeet); Clubfoot (Talipes equinovarus) / 659 510 Chapter 5 � Lower Limb consists of two elements of the decrease limb: the rounded, outstanding posterior region, the buttocks (L. The transition from trunk to free decrease limb occurs abruptly within the inguinal area or groin. Here the boundary between the belly and perineal regions and the femoral area is demarcated by the inguinal ligament anteriorly and the ischiopubic ramus of the hip bone (part of the pelvic girdle or skeleton of the pelvis) medially. During the 4th week of development, the upper limb buds seem as elevations of the C5�T1 segments of the anterolateral physique wall.
Delayed enhancement in (b) two- and (c) four-chamber views demonstrates patchy enhancement (arrows) predominantly within the mid-myocardium within no definitive vascular territory. In either case, the overwhelming majority of sufferers totally recover with supportive administration. Sequelae can happen in as many as one-third of patients and usually contain congestive coronary heart failure secondary to dilated cardiomyopathy. In these situations, extra invasive measures are required for management, including intraaortic balloon pump or ventricular help gadget insertion, or even cardiac transplantation. The depth of myocardial involvement and its distribution sample can favor the prognosis of ischemic over nonischemic damage. Combined coronary and late-enhanced multidetector�computed tomography for delineation of the etiology of left ventricular dysfunction: comparison with coronary angiography and contrast-enhanced cardiac magnetic resonance imaging. It is crucial to distinguish between ischemic and nonischemic causes of myocardial injury, as management and prognosis differ considerably. Ultrasonography can be used to assess practical status of myocardium and detect gross inflammatory changes in wall construction. Deep intratrabecular recesses outcome that are in continuity with the ventricular myocardium. Clinical Features the prevalence of noncompaction inside the general population is 0. Long-standing illness leading to congestive heart failure may lead to an expanded left coronary heart border as properly as pulmonary edema. Contrast-enhanced photographs with gadolinium could present perfusion defects in the noncompacted layer, doubtless secondary to microcirculatory abnormalities. Delayed distinction enhancement can additionally be seen in areas of noncompaction, presumably because of regional fibrosis. Notably, it might be difficult to distinguish between delayed enhancement and the presence of deep recesses. Diagnosis is made by quantitative measurement of the noncompacted myocardium compared to that of the compacted myocardium. How to Approach the Image Echocardiography is often the imaging modality of choice and reveals multiple distinguished trabeculations with deep recesses in continuity with the ventricular cavity. What Not to Miss Thrombus formation may be seen in noncompaction cardiomyopathy, from stasis and/or gradual flow within the deep recesses.
Like the median nerve, the ulnar nerve has no branches within the arm, nevertheless it also provides articular branches to the elbow joint. It is separated from the skin by only the olecranon bursa, which accounts for the mobility of the overlying pores and skin. The triceps tendon is definitely felt because it descends alongside the posterior aspect of the arm to the olecranon. The fingers can be pressed inward on both sides of the tendon, the place the elbow joint is superficial. The proximal a part of the bicipital aponeurosis could be palpated where it passes obliquely over the brachial artery and median nerve. The humeral head may be palpated when the arm is moved while the inferior angle of the scapula is held in place. The brachial artery could additionally be felt pulsating deep to the medial border of the biceps. Medially, the mass of flexor muscular tissues of the forearm arising from the frequent flexor attachment on the medial epicondyle; most particularly, the pronator teres. The flooring of the cubital fossa is fashioned by the brachialis and supinator muscles of the arm and forearm, respectively. If the thumb is pressed into the cubital fossa, the muscular lots of the lengthy flexors of the forearm might be felt forming the medial border, the pronator teres most immediately. The lateral group of forearm extensors (a gentle mass that can be grasped separately), the brachioradialis (most medial) and the lengthy and quick extensors of the wrist, may be grasped between the fossa and the lateral epicondyle. A regular (positive) response is an involuntary contraction of the biceps, felt as a momentarily tensed tendon, normally with a short jerk-like flexion of the elbow. A constructive response confirms the integrity of the musculocutaneous nerve and the C5 and C6 spinal cord segments. Inflammation of the tendon (biceps tendinitis), usually the outcomes of repetitive microtrauma, is common in sports activities involving throwing. This painful condition could happen in young individuals throughout traumatic separation of the proximal epiphysis of the humerus. Rupture of the biceps tendon could end result from forceful flexion of the arm towards excessive resistance, as happens in weight lifters (Anderson et al.
� the fibers of the best crus of the diaphragm kind a sphincteric hiatus for the esophagus at the T10 vertebral level. � the descending aorta and thoracic duct pass posterior to the diaphragm at the T12 vertebral level, in the midline between the crura, overlapped by the median arcuate ligament connecting them. � Superior and inferior phrenic arteries and veins provide a lot of the diaphragm, with additional drainage occurring by way of the musculophrenic and azygos/hemi-azygos veins. � In addition to unique motor innervation, the phrenic nerves provide most of the pleura and peritoneum covering the diaphragm. � Peripheral elements of the diaphragm receive sensory innervation from the decrease intercostal and subcostal nerves. � the left lumbocostal triangle and the esophageal hiatus are potential sites of acquired hernias via the diaphragm. Chapter 2 � Abdomen 321 Fascia and muscular tissues: Large, complex aponeurotic formations cover the central components of the trunk each anteriorly and posteriorly, forming dense sheaths centrally that house vertical muscular tissues and attach laterally to the flat muscular tissues of the anterolateral belly wall. � the endoabdominal fascia overlaying the anterior aspects of each the quadratus lumborum and psoas is thickened over the superiormost aspects of the muscle tissue, forming the lateral and medial arcuate ligaments, respectively. � A extremely variable layer of extraperitoneal fat intervenes between the endoabdominal fascia and peritoneum. � Only the subcostal nerve and derivatives of the anterior ramus of L1 (iliohypogastric and ilio-inguinal nerves) have an stomach distribution-to the muscular tissues and pores and skin of the inguinal and pubic areas. Arteries: Except for the subcostal arteries, the arteries supplying the posterior abdominal wall come up from the abdominal aorta. � the belly aorta descends from the aortic hiatus, coursing on the anterior features of the T12�L4 vertebra, instantly left of the midline, and bifurcates into the frequent iliac arteries on the degree of the supracristal airplane. Lymph vessels and lymph nodes: Lymphatic drainage from the stomach viscera programs retrograde alongside the ramifications of the three unpaired visceral branches of the stomach aorta. � Ultimately, all lymphatic drainage from constructions inferior to the diaphragm, plus that draining from the lower six intercostal areas through the descending thoracic lymphatic trunks, enters the beginning of the thoracic duct at the T12 level, posterior to the aorta. � the origin of the thoracic duct may take the type of a saccular cisterna chyi (chyle cistern).
Taragin Definition Aberrant proper subclavian artery is the most typical aortic arch abnormality, with an incidence of approximately 0. The normal right subclavian artery arises from the division of the brachiocephalic trunk together with the right frequent carotid artery, the primary department of the typical three branches of the aortic arch. In distinction, an aberrant proper subclavian artery arises from the left aspect of the arch as a fourth department. In order to provide its territory, the aberrant artery should cross behind the esophagus, the place it may hardly ever be the source of signs. Clinical Features Patients are mostly asymptomatic, particularly as children. Aberrant proper subclavian artery is taken into account by many to be a standard anatomic variant. When the aberrant vessel is symptomatic, it mostly presents as progressive dysphagia. This is related to vascular compression of the esophagus, a situation referred to as "dysphagia lusoria. Upper extremity ischemia due to vascular compression is an unusual complication of aberrant right subclavian artery that may require surgical procedure. In almost all instances, the aberrant proper subclavian artery happens in the presence of a left-sided ligamentum arteriosum. As this artery only passes and compresses the midline structures posteriorly, no vascular ring is present. In the very rare instance of an aberrant proper subclavian artery occurring together with a right-sided ligamentum arteriosum, a vascular ring can be current secondary to compression from both the posterior and anterior directions. Occasionally, the origin of the aberrant right subclavian artery is a saccular aneurysmal dilatation known as a diverticulum of Kommerell. Anatomy and Physiology Aberrant proper subclavian artery is a developmental anomaly by which the best subclavian artery maintains its embryonic connection to the descending aorta and persists as the fourth and left-most department of the aortic arch, past the ligamentum arteriosum. The proper common carotid artery arises on its own, rather than as part of a brachiocephalic artery.
Redge, 41 years: � Venous drainage from the brain happens through the dural venous sinuses and internal jugular veins.
Hernando, 32 years: While the overwhelming majority of cardiac tumors are metastatic from one other site, almost 75% of major cardiac tumors are benign.
References
Realice búsquedas en nuestra base de datos: