

Daniel Monti, MD
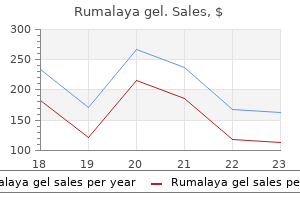
Rumalaya gel dosages: 30 gr
Rumalaya gel packs: 1 tubes, 2 tubes, 3 tubes, 4 tubes, 5 tubes, 6 tubes, 7 tubes, 8 tubes, 9 tubes, 10 tubes

It simply considers the nature of dif ferent forms of object data and the corresponding crossmodality rela tionships for major object domains in larger depth. Outstanding Questions this up to date proposal highlights the affect of the mapping rules between sensory and response sys tems in shaping the representation properties in every system. It frames a line of inquiries to be examined: (1) What is the knowledge content at these domain preferring areas Does the "multimodal" area effect indeed replicate the identical forms of form representa tion Mid-level complex type function representation (object form parts affiliate with domains) Elongation Rectilinear Curvature Low-level visual features Orientation, Color. The primary point is that the mapping between the perceptual representations and various response systems (corresponding to dif ferent object domains) may occur at dif ferent levels, relying on the relationships between methods. Note that the represen tation buildings within the navigation and fight/flight response systems are extremely simplified. Studies of domain representation have focused on the cortical sites the place the area distinction is most visible, such because the so referred to as higher order cortex. Recent neurophysiological evidence from nonhuman primates has discovered neu rons within the major visible and motor techniques which might be tuned to features rather more advanced than beforehand thought, similar to those selective to predators. While the advanced characteristic space for objects is giant and undetermined (Kourtzi & Connor, 2011), these that are optimized for area detection and triggering specific stimulusresponse mappings may be good candidates for the effective functional items. Conclusions For a very long time, the sector of object processing has aimed to determine whether or not domain differences originate from bottomup results or innate domain specific cir cuits. These discussions have led to a more detailed understanding and new questions about the perform alities and connectivity patterns of a range of cortical regions, particularly the higherlevel visual cortex. I want to highlight an additional dimension: the nature of the interface between dif ferent techniques. After all, how the brain parses the physical world is driven by the need for 790 Concepts and Core Domains optimal responses for survival, which is dif ferent for these object domains.
Consequently, informationprocessing affordances may differ profoundly between languages. Scholars disagree about whether, amongst this range, there are universals: properties that maintain for all human languages. However, absolute universals are surprisingly troublesome to find (Evans & Levinson, 2009), as even some seemingly simple assumptions. Implications for the cognitive (neuro)science of language are 1 For counterarguments by proponents of linguistic universals, see. Given this diversity, is it possible to deal with language as a single, unified cognitive area Such typological skewings may be linked to the way during which the mind learns and processes data (Bickel et al. They can thus inform the neuroscience of language by providing targets for rationalization in phrases of cognitive and/or neurobiological mechanisms (for word order, see Bickel et al. Given the tendency of most neuroscientific approaches to assume crosslinguistic unity (or solely examine a small vary of languages), this chapter goals to highlight how the neurobiology of language could additionally be formed by crosslinguistic range. This ought to, nevertheless, not be taken to counsel that mind mechanisms of language processing show no crosslinguistic generalizations at all. Rather, we assume that many primary assumptions laid out in the other chapters of this part maintain throughout the languages of the world. Likewise, all languages should draw on fundamental combinatory mechanisms (see chapter 74) and complex, distributed conceptual representations (see chapter 76). Further compelling proof for crosslinguistic similarities stems from signal languages, which present a extensive range of neurocognitive- processing parallels to spoken languages (see chapter 73). While current years have seen a sharp improve in examinations of language production in understudied and typologically diverse languages (cf. Finally, the chapter aims to current a framework for the crosslinguistic neuroscience of language primarily based on the evidence at present obtainable. To this finish, it draws primarily on domains/phenomena for which systematic crosslinguistic comparisons exist. We first evaluate the results of crosslinguistic range on the processing of linguistic categories earlier than addressing information-processing mechanisms and concluding with a discussion of future instructions.
Mathematically, such a two-level summary chunking capability is sufficient to generate nested tree buildings of unlimited depth, offering that, via a loop circuit, low-level chunks may instantiate high-level chunks in a recursive manner. Such nested tree structures are thought-about to be basic traits of the human college of language (Dehaene, Meyniel, Wacongne, Wang, & Pallier, 2015). Beside manufacturing, language comprehension requires decoding the syntactic structure of sentences. In this view, the same neural circuit comparable to the execution of a single task set is engaged in sentence manufacturing and comprehension with the activation and inactivation of motor outputs, respectively. The proposed human executive system can also provide insights in regards to the emergence of human reasoning (Donoso, Collins, & Koechlin, 2014; Oaksford & Chater, 2009). This new hypothesis serving as actor is then examined as accounting for noticed contingencies. Hypothesis testing is probably the most primary type of backward inference, as the choice to form a brand new actor/hypothesis is subsequently revised in accordance with the acquisition of subsequent data. Backward inferences are certainly important in optimum inferential processes working in open- ended environments for dealing with the intrinsic nonparametric nature of making new latent causes (Teh et al. As end result, task selection might look like maximizing action utility, although the selection is actually based mostly on task set reliability. Parallel organization of functionally segregated circuits linking basal ganglia and cortex. Separate neural substrates for ability learning and per for mance within the ventral and dorsal striatum. Testing the mannequin of caudo-rostral organization of cognitive management in the human with frontal lesions. Cognitive control, hierarchy and the rostrocaudal organization of the frontal lobes. Functional magnetic resonance imaging evidence for a hierarchical group of the prefrontal cortex. Hierarchical cognitive management deficits following injury to the human frontal lobe. In the present principle, as an alternative, actor task sets are chosen or Koechlin: Executive Control and Decision-Making 465 Badre, D. Connectivity-based parcellation of human cingulate cortex and its relation to practical specialization.
The time period usually collapses collectively a number of distinct processes that happen prior to movement. At different times, the time period preparation is used without any rationalization of what exactly it could or might not entail, or whether it even necessarily occurs. A dictionary definition of preparation is "the act of being made ready to be used or consideration. Furthermore, this definition means that preparation pertains to readiness to carry out a particular action, and Is Movement Preparation Time- Consuming An instance of this effect comes from the work of David Rosenbaum (1980), during which human participants have been instructed, by way of a collection of letters, which among eight attainable targets they might have to move to . The extra details about the forthcoming motion was disclosed beforehand, the quicker the reaction times. The interpretation of those findings, which has dominated a lot of the thinking about motion preparation and initiation, is that specifying every parameter of the movement is time- consuming. Precuing some aspect of the required movement allows the corresponding parameter to be specified upfront, allowing the motion to then be generated with a shorter reaction time. As identified by Goodman and Kelso (1980), nevertheless, a serious frailty in this logic is that specifying the motion could not have been essentially the most difficult aspect of this task. This is much longer than the typical response times of 200�250 ms for reaching actions toward a visually presented target location (Haith, Pakpoor, & Krakauer, 2016). It is unlikely, therefore, that the typical reductions in response time afforded by precues are attributable to movement preparation per se. This raises an necessary level about motion preparation: that it ought to only embody processes specific to producing the movement itself, to not deciding which movement to make. Only the specification of the coverage prescribing the precise movement to be generated, contingent upon a specific aim, must be considered movement preparation. With this in thoughts, motion preparation is maybe finest studied via tasks in which the required movement is cued by a extremely salient spatial cue so that deciding what action to take ought to be trivial (though we discuss preparation within the context of decision-making additional below). However, the reduction in response time enabled by direct spatial precues is just of the order of 50�100 ms and can be as little as 30 ms in monkeys (Churchland, Yu, Ryu, Santhanam, & Shenoy, 2006). The time consumed by preparation, therefore, seems to be quite modest and definitely a lot shorter than most classical theories postulate. Movement Preparation versus Movement Initiation Approaches to understanding motion preparation based mostly on examining response times are inevitably indirect and depend on strong assumptions about what determines response occasions.
Recent advances in approaches to lesion evaluation and corroborating data from useful neuroimaging studies of neurotypical subjects have enabled a new understanding of a specialised praxis community in the left hemisphere. After a quick dialogue of conventional accounts, this chapter provides a evaluation of our present neurocognitive understanding of this praxis system. In explicit, three major clusters of behav iors reflecting damage to conceptual, spatiotemporal, and selection-based elements of expert motion planning are mentioned, attributable to posterior temporal, inferior parietal, and frontal community nodes and their interconnections. We conclude by providing suggestions for several future research instructions that can profit the examine of apraxia, its rehabilitation, and our broad understanding of motion imitation and power use. Because much of our understanding of the dysfunction derives from studies of individuals with focal lesions, this chapter is worried primarily with apraxia in lefthemisphere stroke and the way apraxia- a dysfunction at the cognitive-motor interface-has elucidated the illustration and planning of object-related actions within the neurotypical mind and mind. That is, apraxia happens despite the relatively unimpaired planning and programming of specific muscle actions. We (and others) use the term motion quite broadly to refer to visible recollections (hereafter, representations) of what stored actions appear to be, kinesthetic/proprioceptive representations of how familiar actions really feel, summary representations of kinematic shape and movement trajectories, and, importantly, the processes that rework info from considered one of these formats to another and from these formats to motor plans. The time period limb apraxia refers to a cluster of related symptoms, some or all of which can be current in any given particular person. Clinically evident spatiotemporal errors may be seen in precise tool use, though these are probably to be extra subtle. Critically, errors occur regardless of adequate strength and motor control and are distinguished even within the ipsilesional, nonparetic left hand. Deficits in motion recognition are additionally prominent in some patients, indicating that the dysfunction could affect representations of the looks of skilled actions. Some patients current a mix of recognition and production deficits, while nonetheless others are notably prone to errors pantomiming the utilization of instruments associated with competing motion alternate options. The relationship of deficits within the distinguished hallmarks of limb apraxia-imitation of meaningful and/or meaningless actions, pantomime to the sight of tools, "settling on" a single applicable action, and gesture recognition-remains a perplexing challenge for so much of clinicians and researchers.
Syndromes
Neural mechanisms of dual-task interference and cognitive capacity limitation within the prefrontal cortex. Anticipatory biasing of visuospatial consideration listed by retinotopically specific-band electroencephalography will increase over occipital cortex. Mechanisms of persistent exercise in cortical circuits: Possible neural substrates for working memory. It due to this fact becomes very helpful to place consideration and reminiscence dynamics right into a developmental context. Later in childhood, both behavioral and neural indices suggest similarities and variations in how youngsters and younger adults deploy attentional management to optimize upkeep in short-term memory. Influences of attention on encoding into reminiscence are additionally obvious by way of the effects that extremely salient social, attentional biases have on studying and later recall from longer-term reminiscence. In conclusion, assessing attentional development and its dynamics factors to the bidirectional influences between consideration and memory. Placing Interactions between Attention and Memory into a Developmental Time Frame Multiple attentional management mechanisms affect processing by the grownup attentive mind, within the remit of notion and short-term memory all the way to encoding into and recall from long-term memory. Starting from influences on notion, traditional neurocognitive fashions of adult consideration detail the mechanisms by which top- down biases from ongoing task objectives play a key function in resolving the competition arising in complicated visual input (Desimone & Duncan, 1995; Kastner & Ungerleider, 2000). Other basic neurocognitive models additionally emphasize each interactions and distinctions between goal- pushed and input- pushed influences on attentional selection within the adult mind (Corbetta & Shulman, 2002), in addition to how overlapping however separable consideration mechanisms govern behav ior in area by way of spatial orienting, in time by way of alerting processes and over goals by way of executive attention (Petersen & Posner, 2012; Posner & Petersen, 1990). Despite differences within the stage at which every of these proposals function and their many exciting new mechanistic foci (Buschman & Kastner, 2015; Halassa & Kastner, 2017), core to these neurocognitive models is the concept of consideration as a set of biases resolving competitors in a posh visual surroundings and due to this fact constraining further processing into memory. Increasingly, views of how the grownup attentive mind operates have been modified to incorporate influences on consideration by the contents of working objectives or long-term recollections (Chun, Golomb, & Turk-Browne, 2011; Gazzaley & Nobre, 2012). It is, in particular, the interface between consideration and these internally held representations that will be the focus of the present chapter. In the primary part, I detail the position of consideration in shaping short- and long-term reminiscence from infancy into childhood, with a focus on both changing and secure mechanisms, whereas the second part highlights growing evidence of how the contents of short-term and longer-term representations influence consideration deployment across development. From the primary months of life, modifications in attention are indexed by the means in which in which infants more and more management their eye movements. While referring the fascinated reader to fuller critiques on the neural basis of consideration improvement in infancy.
People also tend to make systematic errors when predicting how a liquid will be oriented within a tilted container (Vasta & Liben, 1996) or when indicating which of two objects is heavier after observing a collision between them (Gilden & Proffitt, 1989; Todd & Warren, 1982). Just as with infants, adults hardly ever maintain misconceptions about the ideas of cohesion, continuity, and get in contact with, however judgments of object movement that incorporate gravity and inertia can be extremely idio syncratic. Instead, people might con struct advert hoc theories of bodily behav iors on the fly (Cook & Breedin, 1994) or rely on an incorrect, non Newtonian model of physics (Clement, 1982; McCloskey, Caramazza, & Green, 1980). Recent studies which have examined how people interact with transferring objects shed some gentle on this matter. Using displays like those in Caramazza, McCloskey, and Green (1981), Smith, Battaglia, and Vul (2013) asked folks to predict the path a ball would take after it was clipped from a swinging pendulum. Results from the first task replicated earlier findings that people often make idiosyncratic errors when drawing the trail of the ball. Other work has proven that in quite so much of eventualities, people can be extremely accurate and exact when executing actions on falling objects (Zago & Lacquaniti, 2005). People also perform better at judging how a liquid will behave in a container when asked to imagine the action of tilting the container somewhat than simply giving a verbal description (Schwartz & Black, 1999). It will be the case, then, that the implicit bodily inferences that assist motion tap into information separate from that which we use to explic itly describe or diagram the workings of physical methods. When attempting to catch the ball cut from the pendulum, individuals might place the bin within the right position even without an explicit understanding of why the ball should end up there. Other studies using three dimensional computergenerated stimuli or videos of object interac tions have also discovered more correct physical inferences than related studies that used two dimensional or sche matic stimuli (Flynn, 1994; Hamrick, Battaglia, Griffiths, & Tenenbaum, 2016). The availability of naturalistic cues to the geometry and material properties of objects may be one other factor that promotes entry to implicit (and extra persistently Newtonian) physical information. The errors that people make when explaining the workings of physics nonetheless remain intriguing (Why would implicit and specific bodily predictions draw on distinct information If we are ready to make accurate, approximately Newtonian bodily predictions in a minimal of some circumstances, what mental capabilities help this ability One pro posal is that we possess a psychological "intuitive physics engine" that carries out simulations of physical dynamics (Battaglia, Hamrick, & Tenenbaum, 2013; Ullman, Spelke, Battaglia, & Tenenbaum, 2017). Here, mental simulation refers to enjoying physical dynamics forward in time as a video game physics engine would.
These neurons have a low background-firing price punctuated by temporary, phasic excitations and inhibitions. Following a sequence of reviews describing various circumstances beneath which these phasic firing modulations happen (Schultz, Dayan, & Montague, 1997; for an early evaluate, see Schultz, 1992), seminal computational work identified that many of those responses might collectively be understood as signaling a reward prediction error (Houk & Adams, 1998; Montague, Dayan, & Sejnowski, 1996; Schultz, Dayan, & Montague, 1997). A reward prediction error is the distinction between the reward acquired and the reward that was expected-in different words, a type of feedback that signifies how errant a choice was given its outcome. In laptop science and engineering, reward prediction errors are commonly used to implement reinforcement learning (Sutton & Barto, 1998). In particular, this signal underpins a category of reinforcement-learning algorithms-model-free reinforcement learning-that use unexpected rewards to "stamp in" preceding selections or actions. The relationship between dopamine neurons and reward prediction error signaling has been replicated and extended in monkey and rodent research. Such research typically use duties involving a collection of choices for potential reward, with members selecting between two choices and the probability of reward given each option varying across trials. These tasks are sometimes referred to as probabilisticlearning duties (because the chance of reward given a choice is probabilistically determined) or as two-armedbandit duties, in reference to the gamble that the participant makes on every trial. But there are tons of other kinds of reward-based choices not accounted for by this framework. If-as the model-free theories suggest- decisions outcome from the strengthened tendency to repeat previously rewarded actions, then the ensuing behav iors are anticipated to have an indicator inflexibility. Similarly, should you get pleasure from cake every afternoon but abruptly develop diabetes, a model-free reinforcement-learning 618 Reward and Decision-Making mechanism would rigidly guide you to have the identical recurring sweet cake every afternoon (it having at all times been rewarded in the past), quite than selecting a unique snack appropriate to your new circumstances. Indeed, an extended custom in psychology has aimed to distinguish between behav iors which might be habit-like and others that are extra knowledgeable or deliberative (Dickinson, 1985; Dickinson & Balleine, 2002; Tolman, 1948). In distinction to the model-freelearning algorithms related to the dopaminergic reward prediction error sign, deliberative behav iors are known as model- based selections, after a family of reinforcement-learning algorithms that learn such information (an inner model of the task or environment) and use it to evaluate options and guide decisions (Daw, Niv, & Dayan, 2005). A particular person ordering from a menu and receiving food might in precept be doing so as a end result of that motion has been bolstered in the past or, alternatively, as a outcome of she has information about the predicted consequence and may flexibly select it. Multiple Memory and Control Systems the notion of an inside mannequin that guides selections raises curiosity ing questions about the place this model comes from.
Hub connectivity, neuronal variety, and gene expression in the Caenorhabditis elegans connectome. Bassett and Pasqualetti: Intrinsic Control Capacities of the Human Brain 735 Bassett, D. A network engi neering perspective on probing and perturbing cognition with neurofeedback. Visual interhemispheric communica tion and callosal connections of the occipital lobes. Specificity and robust ness of lengthy distance connections in weighted, interareal connectomes. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of Amer ica, one hundred fifteen, E4880� E4889. Dynamic reconfiguration of frontal brain networks throughout execu tive cognition in people. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 112, 11678�11683. Pro ceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of Amer ica, 113, 12568�12573. Recordings of Caenorhabditis elegans locomotor behaviour following tar geted ablation of single motorneurons. Sex dif ferences in network controllability as a predictor of execu tive function in youth. Context dependent structure of brain state dynamics is explained by white matter connectivity and theories of network control. Cognitive relevance of the community construction of the human brain practical coactivation network. Proceed ings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of Amer ica, one hundred ten, 11583�11588.
Habituation of a monosynaptic response in frog spinal wire: Evidence for a presynaptic mechanism. Learned spatiotemporal sequence recognition and prediction in primary visible cortex. Excitability of cutaneous afferent terminals throughout habituation and sensitization in acute spinal cat. Effects of stimulus frequency and intensity on habituation and sensitization in acute spinal cat. Habituation of the response to sensory stimuli of neurones within the brain stem of rabbits. Drosophila chemoreceptors: A molecular interface between the chemical world and the mind. Contrasting roles for parvalbumin- expressing inhibitory neurons in two forms of grownup visual cortical plasticity. Flexible sensory representations in auditory cortex pushed by behavioral relevance. Behavioral dissociation of dishabituation, sensitization, and inhibition in Aplysia. In Vivo Ca(2+) imaging reveals that decreased dendritic excitability drives startle habituation. Habituation is altered in neuropsychiatric disorders- a comprehensive evaluation with suggestions for experimental design and evaluation. Habituation revisited: An up to date and revised description of the behavioral characteristics of habituation. Dishabituation and sensitization emerge as separate processes during development in Aplysia.
Dudley, 52 years: This is distinguished from model-free reinforcement studying, in which agents study solely in regards to the values of individual actions (Daw, Gershman, Seymour, Dayan, & Dolan, 2011). Encoding processes supporting memory for rewarding info Similar to emotional material, cues that sign a future reward have been proven to improve early perceptual and attentional processes (Bunzeck, GuitartMasip, Dolan, & D�zel, 2011; Gruber & Otten, 2010; Yeung & Sanfey, 2004). The chapter by Stauffer and Schultz suggests, nonetheless, that the dopamine sign seems to reflect utility and thus constitutes a bodily implementation that helps to interpret economic determination processes. A key chal lenge for the sphere, which this chapter attempts to address, is to understand how the spatial information representations revealed by cognitive behavioral research are mediated by neu ral techniques.
Wilson, 51 years: From a lifespan perspective, reminiscence could be thought of as an extension of growth. These contributions present a glimpse of the ways during which computation is bridging the gap between the brain and cognition. The physiology of the circuit was then further characterised by including sensible glutamate receptor channel dynamics and exhibiting how the proportion of these receptor varieties strongly shape sustained delay exercise in prefrontal areas (Wang, 1999). A functionally driven optimization approach has additionally been effective at driving progress in modeling the motor system (Lillicrap and Scott 2013; Sussillo et al.
Gamal, 23 years: Likewise, spatial cues that are previously experienced as unstable have little management over place fields (Knierim, Kudrimoti, & McNaughton, 1995). A individual ordering from a menu and receiving meals would possibly in principle be doing so as a end result of that motion has been bolstered up to now or, alternatively, as a end result of she has information concerning the predicted consequence and can flexibly choose it. The findings could be defined by the functional inhibition of visible areas by alpha oscillations; this inhibition serves to scale back interference from visible stimuli when attending to auditory input. Yildirim, Belledonne, Freiwald, and Tenenbaum (2019) examined their approach in one area of highlevel notion, the notion of faces.
Sibur-Narad, 50 years: However, if details about every object is maximal in, but not restricted to, every phase, it may also be compatible with the flexibleresource model or a hybrid of the 2. This means that the animal infers the "state" of the duty based mostly on observable stimuli (the reward). The property of elongation tends to be correlated with "toolness"-rendering it troublesome to interpret why certain mind areas exhibit differential neural responses to instruments compared to baseline classes, such as animals, faces, and locations. Cognitive management, hierarchy and the rostrocaudal group of the frontal lobes.
Boss, 43 years: Relationship to previous work in visual modeling Other approaches to modeling the visual system could be positioned within the context of the optimization framework. If the tower is unstable, what kind of utilized drive or other motion could maintain it stable Observations on the pathology of human spinal cord harm: A review and classification of 22 new instances with particulars from a case of persistent wire compression with extensive focal demyelination. Thus, an intermediate step in this habituation course of entails the potentiation of excitatory transmission in the cortex.
Umbrak, 45 years: Topographic organization of corticospinal projections from the frontal lobe: Motor areas on the lateral surface of the hemisphere. In distinction, the suggestions pathway to the pulvinar originates in cortical layer 6 of a given area and tasks to an area- specific zone, which itself projects to layer 1 of the identical cortical space. The allowed reaction time (and, consequently, the time available for movement preparation) might be diversified by various the moment at which the goal was introduced relative to this fixed time of movement initiation. Loss of attentional stimulus selection after extrastriate cortical lesions in macaques.
Osmund, 37 years: Categorical notion of somesthetic stimuli: Psychophysical mea surements correlated with neuronal occasions in primate medial premotor cortex. Dopamine seems to underpin these biases, perhaps in coordination with serotonin (Boureau & Dayan, 2011; Cools, Nakamura, & Daw, 2010). Neuronal Activity: Codes and Contents the triple quest of cognitive neuroscience Three challenges should be addressed to isolate the elementary computa tions underlying a given cognitive process (figure 58. But in virtually all circumstances, changing construction also changes the semantic combinatorics.
References
Realice búsquedas en nuestra base de datos: